By Elaine Ellinger from Perspectives on Islam.
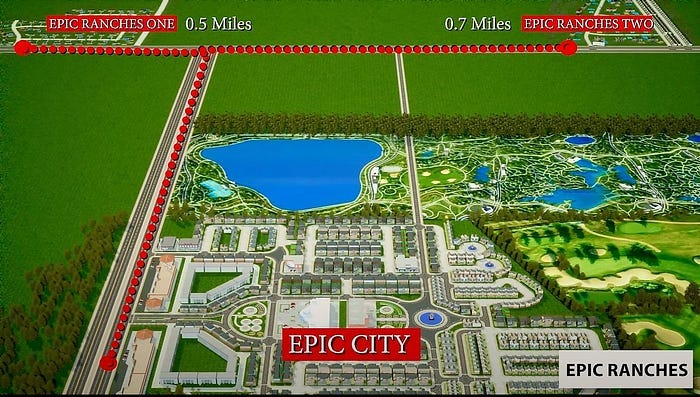
The United States was founded on principles of freedom, equality, and individual rights. Yet today, within its borders, enclaves and entire cities are emerging where a foreign legal system is taking hold — one that directly contradicts the U.S. Constitution. The 402 acre ‘Epic Ranch’ Islamic development in Texas is a recent example [1–3].
The Declaration of Independence states:
We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.”
Why does this reminder matter? Because these rights — once considered inviolable — are now being challenged by an opposing system of governance embedded within the ideology of Islam. This is not merely a religious doctrine but a comprehensive legal, political, and economic system that governs all aspects of life
Islamic law (sharia) mandates punishments that directly violate U.S. constitutional protections, including:
- Execution for apostasy (violating freedom of religion)
- Punishment for blasphemy (violating freedom of speech)
- Legal inferiority for women and non-Muslims (violating equal protection under the law)
- Supremacy of Islamic law over national law (violating the Constitution’s Supremacy Clause)
The Constitution prohibits the government from restricting legitimate religious practice, but it also does not require it to extend protections to belief systems that subvert constitutional rights and undermine the very freedoms it exists to uphold [4].

KEY CONTRADICTIONS:
1. The First Amendment (Freedom of Religion, Speech, and Assembly)
The First Amendment guarantees freedom of religion and prohibits government favoritism or restriction of religious practice. However, Islamic doctrine contains fundamental principles that violate the very freedoms the First Amendment protects:
Apostasy Punishment (Death for Leaving Islam)
Directly violates freedom of religion. No other major belief system mandates death for leaving it.
- Koran 4:89 — “But if they turn back, then seize them and kill them wherever you find them.”
Tafsir (commentary) Ibn Kathir on 4:89 confirms that apostates should be executed unless they return to Islam. - Bukhari 6922 — “Whoever changes his religion, kill him.”
- ‘Reliance of the Traveller: a Classic Manual of Islamic Law’ (ROT) o8.1 — “When a person who has reached puberty and is sane voluntarily apostatizes from Islam, he deserves to be killed.”[5]
- Current Example: Islamic majority countries where apostasy is punishable by death [6]
Blasphemy Laws (Death or Punishment for Criticism of Islam)
Contradicts freedom of speech and freedom of the press.
Punishment: Death for insulting Allah or Muhammad.
- Koran 33:57 — “Indeed, those who abuse Allah and His Messenger — Allah has cursed them in this world and the Hereafter and prepared for them a humiliating punishment.”
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 33:57 — Blasphemers are cursed and should be severely punished in this world. - Dawud 4361 — A blind man killed his slave-woman for insulting Muhammad. Muhammad ruled that no blood money was due.
- Reliance of the Traveller, o8.7 — “Whoever reviles Allah or His Messenger may be killed if he doesn’t repent.”
- Current Example: Blasphemy laws apply to both Muslims and non-Muslims, and in many cases, the punishment is not left to the courts — mobs enforcing sharia often carry out extrajudicial killings [7]. In Pakistan “Nearly 100 people have been lynched to death while dozens remain on death row, according to the U.S. Commission on International Freedom.”
Suppression of Non-Muslim Religious Expression
Islamic doctrine mandates dhimmitude, taxing and subjugating non-Muslims, which directly opposes the First Amendment’s guarantees of religious freedom and equal protection.
Legal and social inferiority for non-Muslims under Islamic rule.
- Koran 9:29 — “Fight those who do not believe in Allah… until they pay the jizya with willing submission and feel themselves subdued.”
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 9:29 explains that jizya must be a sign of humiliation, reinforcing Islamic dominance. - Muslim 1731a — Muhammad took jizya from non-Muslims, ensuring their subjugation.
- Reliance of the Traveller, o11.1–11.3 — Dhimmis are expected to pay ‘jizya’ and accept inferior status preventing them from building new churches, or openly practicing their religion such as visible attire or ringing bells.
- Current Example: In Bangladesh, reports of “Hindu temple vandalism and idol destruction continue to surface”, reflecting ongoing suppression of non-Muslim religious expression. Meanwhile, in Indonesia, churches are frequently targeted for destruction. The situation worsened in 2014, when the Aceh provincial administration passed the Qanun Jinayat [bylaw], imposing sharia law on both Muslims and non-Muslims, further restricting religious freedoms [8].
Censorship of Criticism (Banning ‘Islamophobia’)
Violates the right to free expression, often using “hate speech” laws to silence critics, contradicting U.S. legal precedent that protects even offensive speech (Brandenburg v. Ohio, 1969). This has created a double standard where criticism of anything is permitted — except criticism of Islam [9].
This two-tier policing goes beyond speech laws. For decades in the UK, authorities turned a blind eye to the abuse of thousands of young English girls by Islamic grooming gangs — not out of ignorance, but out of fear of being labeled ‘racist’ [10].
In Toronto, Officers Farhan and Siddiqui explain how they created a course: “The Foundations of Islam and How to Combat Islamophobia” catering to the Islamic community. The course is now mandatory for both uniformed and uniformed officers [11].
2. The 14th Amendment (Equal Protection & Due Process)
The 14th Amendment guarantees equal protection under the law, meaning no person or group should receive special legal privileges or suffer discrimination based on race, religion, or gender. Islam’s doctrine directly contradicts this principle:
Gender Inequality in Testimony & Inheritance (Women’s Testimony Worth Half a Man’s, Sons Inherit Twice as Much as Daughters)
Violates equal protection by legally codifying gender discrimination.
- Men have superiority over women in legal rights, inheritance, testimony, and marriage.
- Koran 4:34 — “Men are in charge of women… and (if they are disobedient) beat them.”
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 4:34 affirms that men have the right to discipline their wives, including physical punishment if they are disobedient. Mohammed said “If I were to command anyone to prostrate before anyone, I would have commanded the wife to prostrate before her husband, because of the enormity of his right upon her.” - Bukhari 304 — “I have not seen anyone more deficient in intelligence and religion than you (women).”
- Reliance of the Traveller, o24.7 — A woman’s testimony is worth half of a man’s.
- Reliance of the Traveller, L6.7 — A daughter inherits half of what a son does.
- Islamic law mandates gender-based inequality in inheritance and testimony. Women receive half the inheritance of men, and a woman’s testimony is worth half that of a man’s in court. These laws are not historical relics — they are actively enforced today in every country where sharia governs family law.
Death Penalty for Apostates & Homosexuals
Violates due process and equal protection, as U.S. law does not permit execution for belief, speech, or private conduct.
Apostasy and Homosexuality are punishable by death according to Islamic law.
- Koran 7:80–84 — The story of Lut (Lot) condemns homosexuality and describes its destruction.
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 7:80–84 explains that homosexuality is a grave sin deserving severe death and that Allah ‘rained on them stones of baked clay’. - Dawud 4462 — “Whoever you find doing the action of the people of Lut, kill the one who does it and the one it is done to.”
- Reliance of the Traveller, p17.3 — “The Prophet said: ‘Kill the one who sodomizes and the one who lets it be done to him.”
- Current Example: Cape Town S. Africa Imam murdered as an apostate for being openly gay. “Hendricks was “an apostate from Islam” and thus should not be prayed over and “should not be buried with the Muslims” … for “homosexuality, the penalty is death” [12].
Sharia Courts Operating with Unequal Standards
Sharia tribunals, enabled by the Federal Arbitration Act (1925), operate in the U.S. under private arbitration agreements [13].
Ongoing Example: In the UK, there are over 85 sharia courts where a woman’s testimony is worth half that of a man’s. In 2019, the EU Parliamentary Assembly reported that [14]:
- “Members of the Muslim community, sometimes voluntarily, often under considerable social pressure, accept their religious jurisdiction mainly in marital issues and Islamic divorce proceedings but also in matters relating to inheritance and Islamic commercial contracts. The Assembly is concerned that the rulings of the Sharia councils clearly discriminate against women in divorce and inheritance cases. The Assembly is aware that informal Islamic courts may also exist in other Council of Europe member States”
3. The Supremacy Clause (U.S. Constitution as the Supreme Law)
The Constitution explicitly states that no foreign law can supersede it (Article VI, Clause 2). However, Islamic doctrine mandates that Sharia must govern all Muslims, directly challenging the supremacy of U.S. law.
Sharia Claims Authority Over National Laws
Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh) states that Sharia is superior to any man-made law, including the U.S. Constitution.
Islamic law must override secular laws.
- Surah An-Nisa 4:59: “O you who have believed, obey Allah and obey the Messenger and those in authority among you…” This verse emphasizes obedience to those in authority, which scholars interpret as rulers who adhere to Islamic principles.
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 4:59 explains that “those in authority” refers to Muslim leaders who implement Allah’s commands, that obedience is due to rulers who govern according to Islamic law. Mohammed said “Even if a slave was appointed over you, and he rules you with Allah’s Book, then listen to him and obey him.” - Koran 5:44 — “Whoever does not judge by what Allah has revealed — they are the disbelievers.”
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 5:44 states that those who judge by secular laws instead of sharia are disbelievers. - Koran 45:18 — “Then We put you, [O Muhammad], on an ordained way concerning the matter [of religion]; so follow it and do not follow the inclinations of those who do not know.”
Tafsir Ibn Kathir on 45:18 Allah said ‘Then We have put you on a (legal) way of commandment. So follow you that.’ - Reliance of the Traveller, a1.1 – ‘the source of legal rulings for all the acts of those who are morally responsible is Allah’ and a1.4 ‘The measure of good and bad… is the Sacred Law, not reason.’
- Reliance of the Traveller, o25.3 — Muslims must obey the ruler as long as he enforces Sharia and does not command disobedience to Allah.
Islamic Finance (Halal Banking & Contracts Prioritizing Sharia Compliance)
Embeds Sharia-based financial structures within U.S. economic systems, undermining secular legal frameworks on spurious claims of ‘religion’ [15].
Legal Precedent & the Government’s Role
Interpretation of the First Amendment. While the government cannot declare an official religion or prevent religious practice, it can establish legal definitions when that status is being abused to undermine constitutional principles.
- The U.S. government has banned specific religious practices when they violate constitutional rights. For example, polygamy — once a core tenet of 7th Day Adventists — was outlawed in Reynolds v. United States (1879) [16].
The Supreme Court ruled that while beliefs are protected, religious practices can be restricted if they violate the law. Congress had long viewed polygamy as incompatible with American values, declaring, “It is the duty of Congress to prohibit in the territories those twin relics of barbarism, polygamy and slavery.” Utah was barred from statehood until the Mormon Church renounced polygamy — something possible because, unlike Islam, their founder was still alive to amend the doctrine [17]. Both of these practices, polygamy and slavery, are ‘halal’ (lawful) according to Islamic doctrine, sharia [18]. - Defining legal parameters for religious protection does not restrict belief but prevents subversive ideologies from exploiting religious freedom to erode constitutional rights.
DISCUSSION:
Islam’s core tenets contradict multiple principles enshrined in the U.S. Constitution. Yet, step by step, sharia is gaining strength in America — not through open conquest, but through gradual legal, financial, and cultural accommodation.
This expansion is taking place through:
- Economic penetration: The spread of Islamic finance and halal industries, embedding sharia-compliant structures into American markets. This includes demands for ‘farm to fork’ halal certification and the use of smartphone apps and social media campaigns to promote compliance. These efforts not only expand market control but also reinforce halal consumption as a marker of Islamic identity, influencing perceptions of what it means to be a “good” Muslim [19].
- Workplace compliance: Demands for Islamic accommodations — such as prayer rooms and religious exemptions — often reinforced by digital apps granting access to activist groups offering free legal representation to ensure such demands are met [20].
- Institutional and Political lobbying: Pressure from activist groups and legal organizations to recognize sharia-based legal rulings, often under the guise of “religious freedom.” In schools where this is not possible citing ‘culture’ as justification.
- Academic capture: Universities offering courses vetted by proponents of Islam and promoting sharia-compliant policies while suppressing critical discussion under the banner of “diversity and inclusion” [21].
- Corporate complicity: Large tech companies, organizations and businesses bending to Islamic pressure, suppressing discussion and dissent in exchange for market access.
- Parallel Legal and Territorial Systems:
- Sharia courts handling family and civil disputes outside the national legal framework.
- ‘Waqf’ land dedications, where land is placed in an Islamic endowment, akin to a change in sovereignty, ensuring that it remains permanently under Islamic jurisdiction [22].
- Community-based “policing”, where Islamic patrols enforce dress codes, restrict alcohol, and pressure businesses and individuals to conform to sharia.
- No-go zones for non-Muslims and law enforcement, where hostility and lack of cooperation deter authorities from intervening [23].
- Koran 13:41 ‘Have they not seen that We set upon the land, reducing it from its borders? And Allah decides; there is no adjuster of His decision.’
These are not abstract concerns. Sharia is not just religious law — it is an alternative governance system that undermines constitutional principles at every level.
CONCLUSION:
In spite of the foregoing, Islam is granted protected status as a ‘religion’ — ignoring the fact that Islam is a socio/political/economic system of governance — complete with it’s own taxation system that finances jihad. Islam does not seek equal coexistence — it seeks dominance [23]. Through civilizational jihad, it is actively reshaping the political and legal landscape of the United States and other Western nations.
Under U.S. law, religious protection is not absolute. The Supreme Court has ruled that religious practices that violate constitutional principles are not immune:
- Polygamy was banned (Reynolds v. United States, 1879), despite being a core practice of early Mormonism.
- Human sacrifice and other criminal acts remain illegal, regardless of religious justification.
The time has come to define the limits of religious protection. A belief system that imposes a foreign legal code, strips individuals of their constitutional rights, and seeks to supersede the U.S. legal system cannot be granted legal privilege as a means to accomplish this.
Had the Founding Fathers foreseen a system that operates not just as a faith, but as an alternative form of governance, they would have drawn clear boundaries from the outset. A legal definition of “religion” within the Constitution itself — one that protects faith but prevents ideological systems from exploiting the very freedoms they invoke as a shield to undermine.
People can call Islam a religion if they choose, but when it comes to protected legal status, there needs to be a qualifier. These privileges are granted at the discretion of the state, not by divine right.
Elaine Ellinger’s Biography
Ms Ellinger‘s interest in Islam began in 1983 owing to a chance encounter with a Bahai refugee who fled Iran during the revolution. At that time, Ms Ellinger was working as a child protection Social Worker in Canada. Since then she has spent many years researching, writing and speaking about the growing influence of sharia in non-Islamic countries from the perspective of the non-Muslim. F
Formerly, Canadian Director and senior researcher for a European think-tank focused on Islamic doctrine, she founded the ‘Perspectives on Islam Society’ in 2023 for the express purpose of providing public education on the primary teachings of Islam in the context of current events.
SOURCES:
[1a] Texas
[2] New Jersey https://rairfoundation.com/new-jerseys-first-islamic-city-muslim-politicians-seize/
[4] https://constitutioncenter.org/media/files/constitution.pdf
[6] https://www.indy100.com/news/the-countries-where-apostasy-is-punishable-by-death-7294486
[7] https://www.rferl.org/a/pakistan-blasphemy-death-sentence-online-posts/33288568.html
[9] https://supreme.justia.com/cases/federal/us/395/444/
[11] https://x.com/DahliaKurtz/status/1899253971480441196?t=ufYvx4kaJPbKhl03mBbP8Q&s=19
[13] https://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/text/9
[14] EU Parliamentary Assembly #8: https://assembly.coe.int/nw/xml/XRef/Xref-XML2HTML-en.asp?fileid=25353
[15] Sookhdeo, Patrick ‘Understanding Shari’a Finance — The Muslim Challenge to Western Economics’ Isaac Publishing 2008
[16] https://supreme.justia.com/cases/federal/us/98/145/
[17] https://archives.utah.gov/2021/05/27/utahs-road-to-statehood-the-obstacle-of-polygamy/
[18] https://perspectivesonislam.substack.com/p/chattel-slavery-is-halal
[19] Video: Halal marketing
[20]
[22] https://perspectivesonislam.substack.com/p/waqf-properties-and-militarization
[23] Kassam, Raheem ‘No Go Zones’, Regnery Publishing 2017
[24] Video: Muslim Domination of U.S. Politics Imminent https://www.bitchute.com/search/?query=islamic%20leader%20declares%20domination&kind=video&sort=new
RELEVANT DOCTRINE:
Koran 4:89 https://legacy.quran.com/4/89
Tafsir 4:89 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/4.89
Koran 33:57 https://legacy.quran.com/33/57
Tafsir 33:57 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/33.57
Koran 9:29 https://legacy.quran.com/9/29
Tafsir 9:29 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/9.29
Koran 4:34 https://legacy.quran.com/4/34
Tafsir Ibn Kathir https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/4.34
Koran 7:80–84 https://legacy.quran.com/7/80-84
Tafsir https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/7.80
Koran 5:44 https://legacy.quran.com/5/44
Tafsir 5:44 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/5.44
Koran 45:18 https://legacy.quran.com/45/18
Koran 4:59 https://legacy.quran.com/4/59
Tafsir 4:59 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/4.59
Koran 45:18 https://legacy.quran.com/45/18
Tafsir 45:18 https://quranx.com/Tafsir/Kathir/45.18
Bukhari 6922 https://sunnah.com/bukhari:6922
Dawud 4361 https://sunnah.com/abudawud:4361
Muslim 1731a https://sunnah.com/muslim:1731a
Bukhari 304 https://sunnah.com/bukhari:304
Dawud 4462 https://sunnah.com/abudawud:4462
Dawud 3592 https://sunnah.com/abudawud:3592
Reliance of the Traveller: a Classic Manual of Islamic Law (sharia) (o8.1, o8.7, o11.1–11.3, m3.7, m5.1, p17.2, o25.3, w4.1, o25.3)
The post Islam Is Inconsistent With The U.S. Constitution (Video) appeared first on RAIR.